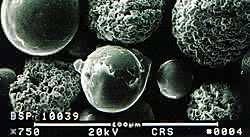
Molybdenum metal is usually produced by powder metallurgy techniques in which Mo powder is hydrostratically compacted and sintered at about 2100°C. Hot working is done in the 870-1260°C range. Moly forms a volatile oxide when heated in air above about 600°C and therefore high temperature applications are limited to non-oxidizing or vacuum environments.
Moly alloys have excellent strength and mechanical stability at high temperatures (up to 1900°C). Their high ductility and toughness provide a greater tolerance for imperfections and brittle fracture than ceramics.
The unique properties of molybdenum alloys are utilised in many applications:
- High temperature heating elements, radiation shields, extrusions, forging dies, etc;
- Rotating X-ray anodes used in clinical diagnostics;
- Glass melting furnace electrodes and components that are resistant to molten glass;
- Heat sinks with thermal expansivity matching silicon for semiconductor chip mounts;
- Sputtered layers, only Ångstroms (10-7 mm) thick, for gates and interconnects on integrated circuit chips;
- Sprayed coatings on automotive piston rings and machine components to reduce friction and improve wear.
For specialised applications, Mo is alloyed with many other metals:
- Mo-tungsten alloys are noted for exceptional resistance to molten zinc;
- Mo is clad with copper to provide low expansion and high conductivity electronic circuit boards;
- Mo-25% rhenium alloys are used for rocket engine components and liquid metal heat exchangers which must be ductile at room temperature.
For more information see also: